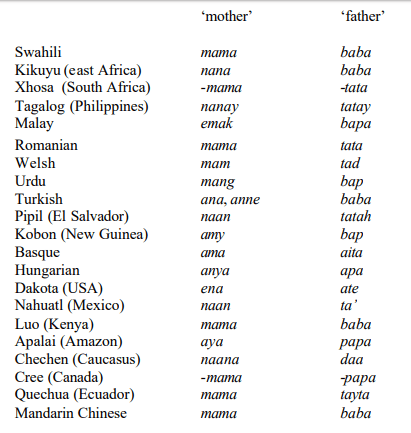
Why are there so many languages that call mother mama ? Is all this just a coincidence? Or what kind of language secrets are there? Today we are going to solve the mystery caused by the two words mama
How many languages call mother mama? Linguist George P. Murdoch once surveyed 470 languages and found that 52% of the words addressing mother in these languages contained ma, me, or mo, while only 15% of the words addressing father contained ma, me , Or mo. He further found that 55% of the words used to address fathers in these languages contained the sounds of pa, po or ta, to, but only 7% of the words used to address mothers contained the sounds of pa, po, ta, to. The picture below lists some languages as examples. We did find that almost all words called mothers contain the sound of ma, while most words called fathers have the sound of pa or ta.
Assuming mama/papa exists in the original language
Linguists first assume that mankind had a common language long, long ago, and all subsequent languages developed from this common language. As for how long ago this common language is a language, no one knows at present, but it can only be assumed that it might have existed in the Homo sapiens era 100,000 years ago. So far, because the Indo-European language family (Indo-European) is the most extensive and in-depth language family studied by linguists, linguists have constructed a hypothetical Proto-Indo-European language based on comparative linguistics. European), this is also the common ancestor of the Indo-European languages constructed by linguists.
So, let’s assume that mama/papa already exists in the original Indo-European language, and it has been passed down to this day! This hypothesis seems perfect: “A long, long time ago, humans had one of the earliest languages. This language is called mama for mother and papa for father, and it has been passed down to this day.”
But in fact, linguistics has an important concept that will overturn this assumption. Before that, let’s take a look at a word that is similar in meaning to mama-“woman” for women. Below we list the words representing woman in seven different Indo-European language families:

The corpora above are all languages belonging to the Indo-European language family. When we tried to find the source of these words, we found that the vocabulary of “woman” in each Indo-European language is different, and some of them are even very different. It is difficult to infer that the word “woman” in the original Indo-European language is What it looks like.
However, there are still linguists who have tried very hard to use comparative linguistics to infer that the form of “woman” in primitive Indo-European languages is: *gwena. Seeing this, we find that among the seven Indo-European language families in the above table, it is difficult to find the language features common to ∗gwena. Because the language has evolved over thousands of years, the font, semantics, and pronunciation may have all changed.
The important concept of linguistics brought out here is: language will change constantly. Assuming that the two words mama/papa already exist in the original language, then, when we see the words representing mother/father, it will definitely not be mama/papa, because the language is always changing and it is impossible to pass Nothing has changed for thousands of years.
The first pronunciation from a child: mama/papa
According to the analysis of linguist Jakobson, provide an answer that most people agree with. Jakobson can be said to be a pioneer in the study of children’s language acquisition. According to his argument, the two words mama/papa are probably created by the child’s parents.
First, let us briefly introduce two stages of children’s language acquisition: the cooing period and the babbling period.
When children are about one month old, they enter the so-called “cooing” period. Babies at this stage will start to make some sounds, but these sounds cannot be distinguished from the meaning, so parents will not think that their children are in speak.
From three to four months, they enter the “babbling period”. At this stage, children begin to pronounce sounds that can be recognized by adults, including some vowels and consonants, and gradually appear repeated syllables.
Divided into consonants and vowels, the easiest vowel to be pronounced is [a], because you only need to open your mouth, vibrate the vocal cords, and send out airflow, and the sound will come out. You hardly need to move your tongue and lips; the consonant is [m] , [B], [p].
Therefore, [ma], [pa], [ba] can be said to be the easiest pronunciation combination.

When the child utters the mama sound, the mother will be very excited to think that the child is interacting with him, and think that the child is calling her instead of calling the family dog, food on the table, etc. Then, the mother will begin to think that this is the first word his child said, “Mama, papa” is a common baby talk between parents and children.
Our mama target is great, let us bless her together